Circular economy: definition, challenges and the role of refurbishment
11/02/2026
0 comments

For decades, our economic model has relied on a linear logic: extract, produce, consume, discard. This approach, built on the assumed abundance of resources, has led to increasing pressure on raw materials, a surge in waste generation, and the accelerated degradation of ecosystems.
In response to these limits, the circular economy introduces a paradigm shift: transforming a one-way model into a virtuous loop system where resources are optimized, products are repaired, reused or recycled, and value is preserved for as long as possible.
👉 Although the term circular economy is now widely used, it is still sometimes misunderstood. This article aims to clarify what the circular economy truly means, explain its practical application to the electronics sector, and analyze the strategic role of refurbishment in extending the second life of tech products.
What is the circular economy?
1. Definition of the circular economy and the limits of the linear model
The traditional linear economic model follows a simple sequence: extract raw materials, manufacture, consume, and then dispose. Once a product reaches the end of its life, its value disappears and it becomes waste. This system increases the extraction of natural resources and mechanically drives up waste generation.
In contrast, the circular economy aims to keep products, components, and materials within the economic cycle for as long as possible. It is based on sustainable design, repair, refurbishment, reuse, and, as a last resort, recycling.
👉 The objective is clear: reduce dependence on raw materials and limit environmental impact at every stage of the product life cycle.
This loop-based system can be visualized through the circular economy diagram down below, which illustrates the interconnection between design, production, use, collection, and the reintegration of materials into a new value cycle.
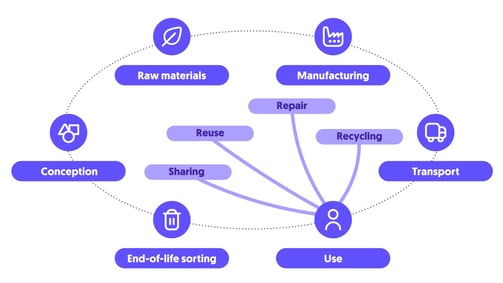
In practical terms, this approach is based on the principles of the “7Rs,” which now structure industrial strategies and business models oriented toward circularity:
- Sustainable sourcing,
- Eco-design,
- Industrial and territorial ecology,
- Functional economy (product-as-a-service models),
- Responsible consumption,
- Extending product lifespan (reducing consumption, reuse, repair, refurbishment, and repurposing),
- Recycling.
2. The evolution of the circular concept: from the 1960s to European regulation
- A theoretical vision (1960s):
The foundations of the circular economy were laid by visionaries such as the economist Kenneth Boulding. He introduced the idea of a “closed-loop” economy, in which the waste of one process becomes the resource of another. In doing so, he established the conceptual basis of circularity.
- The “cradle to cradle” approach (1990s):
Later, the concept of “cradle to cradle” was developed by Michael Braungart and William McDonough. It focuses on eco-design: products should be designed from the outset to be dismantled, repaired, and recycled.
The term “circular economy” itself was first used in 1989. Over time, it gained visibility and importance, driven by rising raw material prices, economic crises, and growing environmental awareness.
- Regulatory institutionalization (from the 2010s onward):
Gradually, the circular economy became a structuring framework for European and French public policies. Here are some examples:
| Measure | Adoption date | Explanation |
| European WEEE Directive (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) | 2012 | Revision of the original directive in force since 2003, setting higher targets in terms of producer responsibility, collection, reuse, and treatment of electronic waste. |
| European Green Deal | 2019 | A comprehensive set of measures designed to put the EU on the path toward ecological transition, with the objective of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. |
| AGEC Law (Anti-Waste for a Circular Economy) | 2020 | A major turning point in France, this law aims to combat waste, promote reuse and repair, strengthen producer responsibility, and improve consumer information. |
| CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive) | 2022 | Explicit inclusion of the circular economy as a component of corporate sustainability reporting requirements. |
Why has the circular economy become strategic for businesses?
1. Circularity: a major challenge faced with the explosion of electronic waste
The technology sector sits at the heart of circular economy challenges. Electrical and electronic equipment represents one of the fastest-growing waste streams worldwide.
In France, according to INSEE (ADEME data, 2023):
- 1,965 thousand tonnes of household electrical and electronic equipment were placed on the market (equivalent to 971 million devices).
- 845 thousand tonnes of WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) were collected.
- The collection rate reached 47% in 2023, compared with 49% in 2020.
- The European regulatory target is set at 65% (Directive 2012/19/EU).
👉 The sector therefore remains significantly below regulatory targets.
However, tightening regulations are reinforcing the need to structure large-scale models for electronic device trade-in, reuse, and refurbishment of electronic equipment.
To better understand the order of magnitude involved, here are the key differences between new and refurbished electronic devices:
| Smartphone | Tablet | Laptop | |
| WEEE production | - New: 94 kg - Refurbished: 13 kg → 81 kg of CO₂e saved |
New vs refurbished: 80.1 kg saved |
New vs refurbished: 126.7 Kg saved |
| Water consumption | - New: 28 m3 eq - Refurbished: 6,79 m3 eq → 21.2 m3 eq saved |
New vs refurbished: 22.9 m3 eq saved |
New vs refurbished: 36.3 m3 eq saved |
| Raw materials | - New: 66 g - Refurbished: 11 g → 55g avoided |
New vs refurbished: 120 g avoided |
New vs refurbished: 314 g avoided |
2. A true performance driver for tech companies
Beyond environmental considerations, the circular economy represents a competitive advantage for professionals. It acts on several strategic levers, including:
- Cost reduction through trade-in programs and the refurbishment of electronic devices,
- Innovation and competitiveness by offering differentiated take-back and refurbishment solutions in the market,
- Enhanced brand image and customer loyalty,
- Improved asset value recovery and better lifecycle management of devices,
- Greater resilience to raw material shortages and supply chain disruptions.
Discover our full analysis of the circular economy for tech professionals by reading our article on the benefits and performance drivers for technology players.
How does Dipli help tech professionals easily implement the circular economy in the electronics market?
1. The all-in-one platform that simplifies the circular tech value chain
Implementing the circular economy in the technology sector faces three major challenges:
- Collecting preowned devices is complex.
Taking back used equipment at scale, seamlessly and across all channels, is a significant operational challenge.
- Purchasing refurbished stock is risky.
Sourcing often lacks standardization in terms of quality, grading, compliance, and consistent availability.
- Device value disappears in between.
Between take-back, sorting, refurbishment, and redistribution, part of the device’s value can be lost due to poor coordination. Too many intermediaries and opaque processes create a “black box” effect.
💡 Dipli addresses these challenges through a standardized platform that simplifies circular tech by structuring and managing it end-to-end:
- An all-in-one platform.
Centralize all your circular operations in one place to manage and optimize your electronic value chain.
- A trusted ecosystem.
Access a certified network of buyers, sellers, and logistics partners to ensure reliable transactions and smooth device flows.
- Data-driven management.
Analyze, compare, optimize, and simplify your workflows and operations by measuring your performance.
👉 Dipli transforms a fragmented chain into a structured, secure, and high-performing trade-in and refurbishment supply chain.
2. An intelligent platform, three circular solutions, serving professionals
Dipli helps you orchestrate your circular tech value chain. The platform acts as a central hub designed to industrialize circularity for players in the electronics market, relying on three complementary services:
1️⃣ Trade-in: for seamless buyback programs.
Dipli enables the deployment of high-performing trade-in programs, capable of scaling device collection and optimizing the resale of used equipment. Collecting and reselling devices at scale and at the best possible value becomes simple and efficient.
2️⃣ Refurbished On Demand: for access to qualified devices.
Professionals can source high-quality, secure refurbished products from trusted partners, significantly reducing the risks associated with refurbished procurement.
3️⃣ Market Data Lab: for real-time data insights.
Dynamic dashboards and strategic insights allow you to monitor performance, optimize margins, and make informed decisions based on reliable, real-time data.
👉 By structuring take-back, refurbishment, and redistribution within a constantly evolving technological environment, Dipli simplifies the electronic value chain and accelerates the adoption of the circular economy among professionals.
Looking to develop the circular economy within your company?
Dipli simplifies the second life of electronic products.
An all-in-one tool for distributors, leasing companies, telecom operators and companies to manage the entire value chain in one place.
The platform connects the electronics industry to secondary markets; simply and securely. Trade-in and return management, refurbishment, omni-channel purchasing and distribution: Dipli covers and simplifies all stages of the circular economy.




Comments (0)